PositionBasedAngle¶
A converter from mechanical position to electrical angle, using the number of pole pairs or the distance between pole pairs.
The PositionBasedAngle processing block can be found in the ‘Templates’ feature in the PMP installer.
In cases where the electrical angle cannot be read directly from a drive, a position-based angle processing block can be used to calculate the electrical angle from its mechanical position. The method by which this processsing block determines the electrical angle depends on whether the drive is linear or rotary.
For a linear drive, the electrical angle will pass through one cycle if the drive traverses a distance equal to the distance between a north and south magnetic pole pair. Thus, the electrical angle can be determined from the position of the motor and the distance between pole pairs.
For a rotary drive, the electrical angle will pass through a number of cycles equal to the number of north and south magnetic pole pairs in a full rotation of the shaft. Thus, the electrical angle can be determined from the rotary position of the shaft, the rotary distance required for a full rotation and the number of pole pairs along the rotation.
Description¶
The implementation of the processing block is shown in Implementation of the PositionBasedAngle processing block.
Implementation of the PositionBasedAngle processing block¶
Two potential configurations of PositionBasedAngle for different drive types are shown in Position-based angle configuration for a rotary drive with four pole pairs (left) and a linear drive (right)..
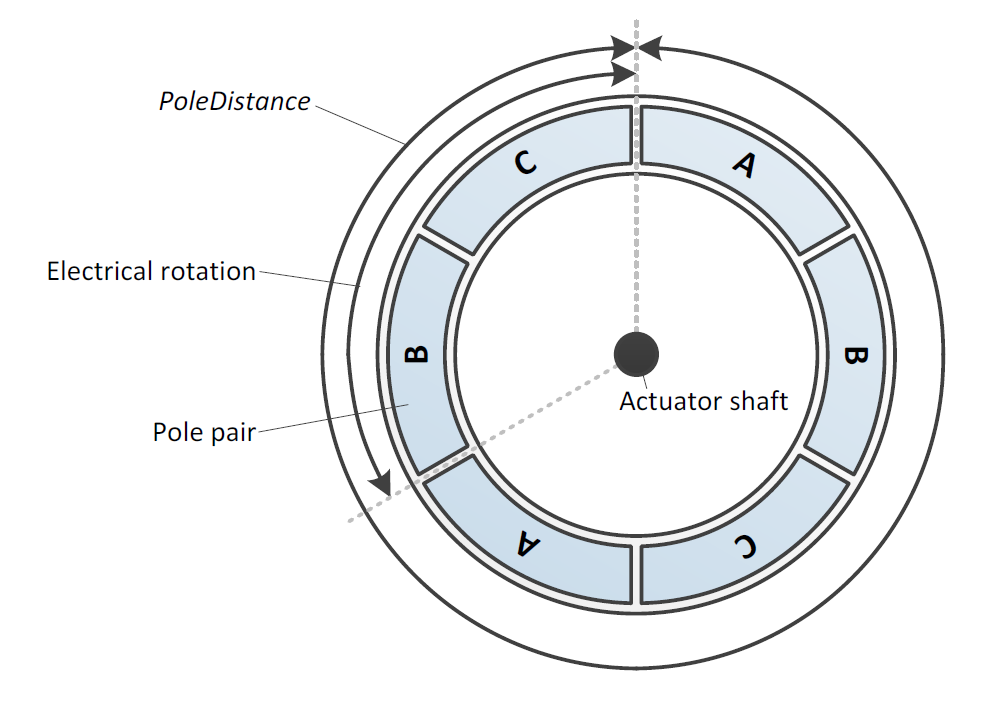
Position-based angle configuration for a rotary drive with four pole pairs (left) and a linear drive (right).¶
Interface¶
Read-write signals¶
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
PoleDistance |
For linear drives, the distance between pole pairs, using the same unit as the |
PolePairCount |
For linear drives, use 1. For rotary drives, the number of pole pairs in a full rotation. |